Column and Row based database
Published on 14 Jul 2023 | Categories: Backend Database
According to the classification of data storage, databases can be categorised as row based database and column based database. Row based database are very simple, infact in most cases they satisfy our requirements. Database like Postgres, MySql store their rows data along with all column fields in different contiguous memory location. Which means Row1, Row2, Row3 would have different memory block in some physical storage. Different row different memory location.
CREATE TABLE clicks (
click_id int,
website varchar,
datetime timestamp
PRIMARY KEY (click_id)
)
INSERT INTO clicks (1,'www.google.com',now());
INSERT INTO clicks (2,'www.facebook.com',now());
INSERT INTO clicks (3,'www.twitter.com',now());
We will take above queries and demonstrate how rows are represented internally in physical storage.
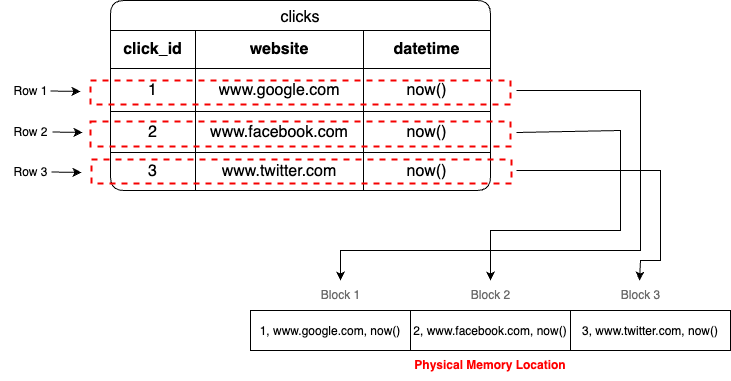
Due to their internal structure row based databases are optimised when you want to fetch information about all columns of a single row. But if you want to fetch data from millions or billions of rows then there would be millions of memory blocks scans and database would not scale efficiently.

In contrary, Column based databases store different column fields in different contiguous memory locations. Which means a single memory block would contain all data values inside one column. Taking example of above table, Each column click_id, website, datetime would have different memory block in some physical storage.
Internally data is stored like below in column based databases.
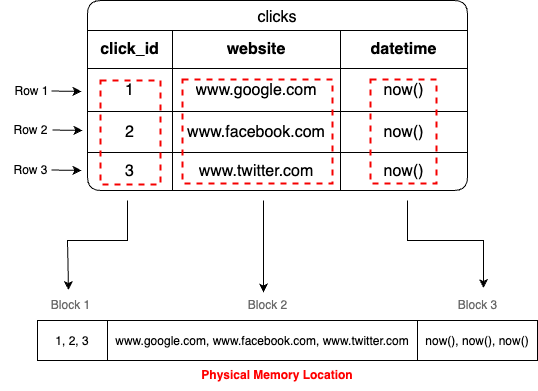
The main catch here is, now if you want to select or aggregate millions or billions of rows of a column then it would be a super optimized operation because all the data of a column is present on single memory block and it would be fetched all at once. No more rows scanning required.

But there are some things that you need to take care of while using column based databases. Always specify columns from which you want to fetch data. Traditional SELECT * would not scale well, as database would scan each memory block to fetch data. Column based databases are designed for Online analytics processing (OLAP), data which has millions of scale, if you try to do transactional stuff (ACID) then they would not behave as expected.